FUMAPEST Pest Control has more than 48 years practical experience in protecting buildings from termite infestations. For your protection phone 1300 241 500 to arrange for a thorough FUMAPEST inspection and report to Australian Standard 3660.
A major economic pest: Recent industry surveys suggest about one third of all unprotected properties in NSW are subject to attack by subterranean termites. Most of the latest technology for termite control products comes from the USA where termite control is a US$5 billion industry.
Most homes are at risk - particularly in built-up urban areas or where well established gum trees are within a 100 metre radius of the building.
The problem is getting worse: Severe termite damage to Australian homes is on the increase since the removal in 1995 of long lasting soil barrier chemicals; the more common use of softwood building and other landscaping timbers that termites find irresistible, such as, timber mulch and railway sleepers.
Other factors that promote rapid termite colony development - automatic watering systems - timber landscaping and maintenance - and building designs that allow hidden termite entry into a building.
|
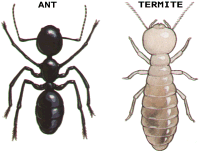
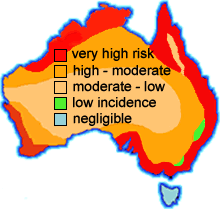
Termites live in the ground and can eat your house down
Termites are known to destroy the wall and roofing timbers of a home within 3 months of construction. Termites cause more damage to homes in Australia than fire, floods, storms and tempest, combined. Termites occur throughout NSW, with a high incidence of attack in virtually all urban areas. CONSUMER NOTE: The standard Home and Building Insurance Policy will NOT cover the repair costs of termite infested structural and decorative timbers. |
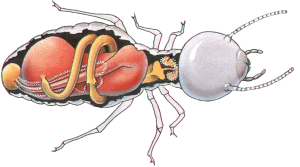
Fascinating biology: Australian subterranean termites evolved more than 250 million year ago. They inhabited Australia long before flowering plants. Their survival success depends on living in a protective underground environment. In some species, their colony nest has a hardened shell, exposed above ground level. In most destructive species in NSW their nest is totally out of sight, below ground level.
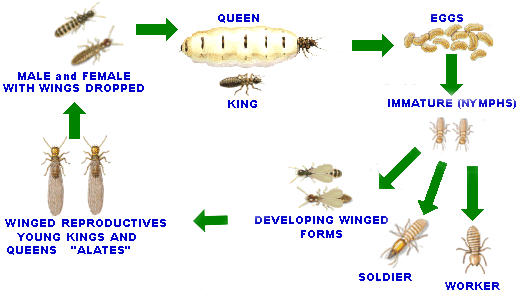
Worker termites build mud-tubes over hard objects. The tubes or "galleries" are made up of partly digested timber and mud excrete, and is moist if currently in active use. The termites keep it's colony nest and galleries at 25 to 35oC with high humidity. If they are exposed to light or open air they will dehydrate and die. Subterranean termites live in constant darkness, excepting for the annual summer swarms of the winged reproductives to set up new nests in the surrounding area.
A million termites in the nest: In some destructive species, a termite colony nest may contain more than a million termites, consisting of a queen, king, young immature nymphs, workers, soldiers and winged reproductives (called alates). Termites are delicate, soft bodied and small in stature, about half the size of match-head, but are highly efficient timber recyclers - Mother Nature's best builders.
The worker termites are blind and forage in a largely random criss-cross fashion looking for new timber food sources. However, they may encounter and follow moisture zones and trail along solid objects, such as, the concrete slab edge of your home. The soldiers accompany the workers in their constant search for new timber food sources. If you find termites active in timber framing, it is the soldiers that rush out to defend the workers.
Experience counts: It takes many years of termite control field-work experience to get a proper understanding of the habits of the destructive termite species habits and their likely foraging areas in a variety of building types and environmental circumstances.
Picture on your left shows a FUMAPEST termite inspector examining a large subsidiary nest, termites built inside the dining room wall cavity of a home. Above ground nests Termites often build such above-ground nests provided there is a reliable moisture source, such as, from faulty plumbing, leaking pipes, shower recess, guttering, broken roof tiles and the like. Mud shelter tubes - picture on left shows a termite mud shelter tube built over a brick foundation wall to the flooring timbers in the sub-floor of a home. Termites are very secretive and will often enter a building through areas inaccessible to inspection, such as, via on-ground patios, cracks or expansion joints or around concrete slab flooring, particularly if the slab edge is obscured by pathways or garden beds. Tiny entry points Termites can pass through a 2 mm crack in concrete slab on-ground flooring and eat through rubber compound between adjoining concrete slabs. Termites often travel under parquetry and other floor tiles to get to the wall and roofing framing timbers. |